Describe the 6 Step Process Used in Gene Splicing
1 Splicing allow for a process called alternative splicing in which more than one mRNA can be made from the same geneAlternative splicing of precursor mRNA is an essential mechanism to increase the complexity of gene expression and it plays an im. Genes are DNA sequences that code for protein.
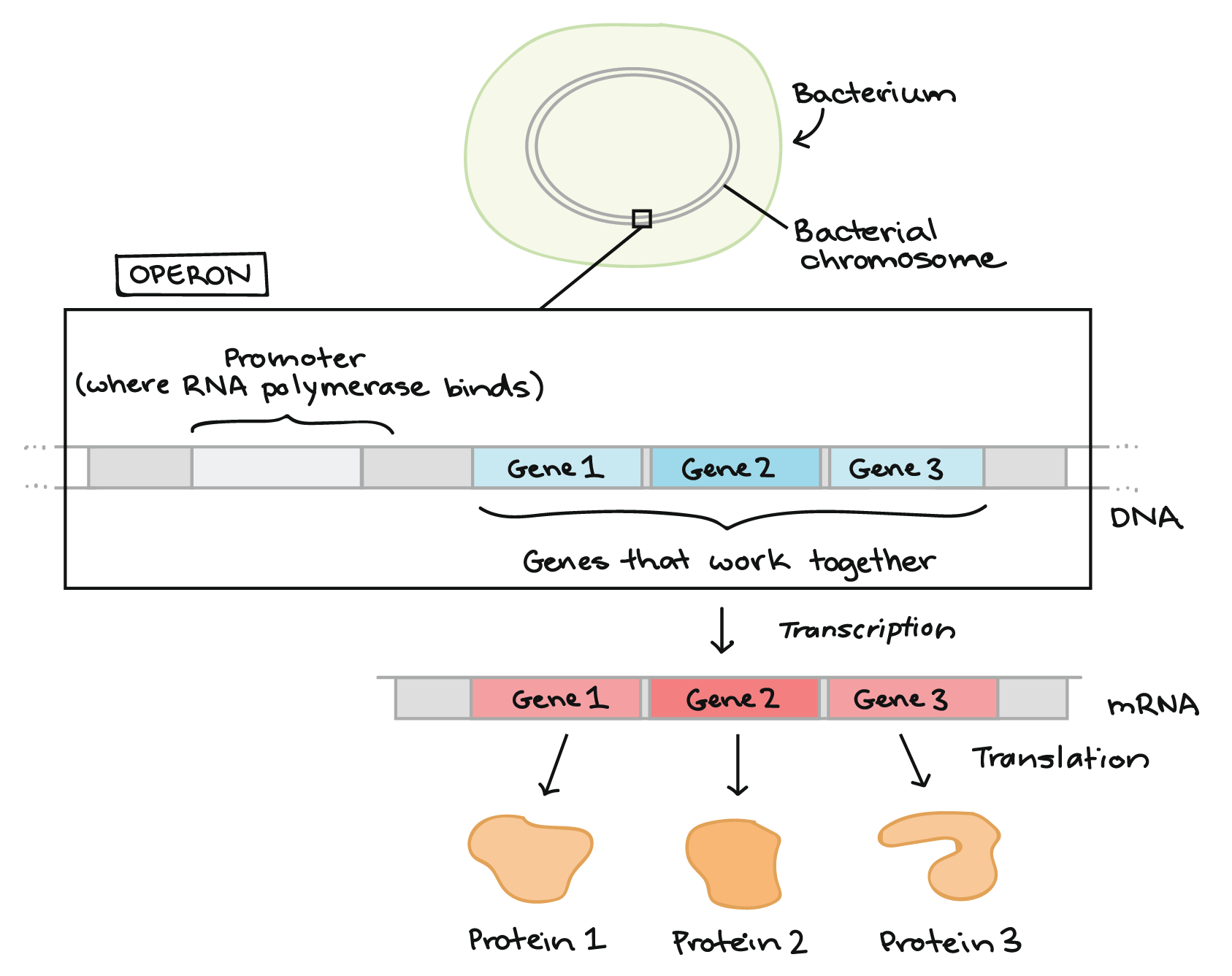
Overview Gene Regulation In Bacteria Article Khan Academy
Now that youve got your genes the next step is inserting them into the plants.
. The main difference between RNA splicing and alternative splicing is that the RNA splicing is the process of splicing the exons of the primary transcript of mRNA whereas the alternative splicing is the process of producing differential combinations of exons of the same geneFurthermore RNA splicing is responsible for the production of a mRNA molecule that can. What type of proteins change RNA splicing patterns. The next step is to isolate the candidate gene.
Pre-mRNA is processed in the nucleus in conjunction with RNAs and. Applications of gene splicing. Krainer explains the connection between SMA and RNA splicing.
A permanent joint formed between two individual optical fibers in the field or factory is known as a fiber splice. Gene splicing involves cutting out part of the DNA in a gene and adding new DNA in its place. Answer 1 of 2.
These segments can then be extracted through gel electrophoresis. For long distance communication it is necessary to join two fibers. Describe RNA interference and the step-by-step process of how siRNA is created and degrades RNA.
Gene splicing is one of the important step in central dogma of eukaryotic cells Gene splicing is a post-transcriptional modification in which a. A specific restriction enzyme will split apart a specific strand of DNA leaving behind a gap in the genetic. Start studying 6 Steps of eukaryotic gene expression regulation.
Gene splicing is a form of genetic engineering where specific genes or gene sequences are inserted into the genome of a different organism. The Connection Between SMA and RNA Splicing. Addition of a poly-A tail tail of A nucleotides to the end of the RNA.
Sharp explains the process of RNA splicing. Depending on the type of restriction enzyme used different parts of the genetic code can be targeted. Many genes contain multiple exons as well as multiple introns.
In order to get the maximum splicing efficiency the fiber should satisfy following criteria. Later stages of gene expression can also be regulated including. 3 5 Explain the significance of alternative splicing in regulating gene expression.
Mix the DNA fragments the cut plasmids and DNA ligase to prod. After splicing a 5 cap and a. The presence of introns is thought to assist gene regulation by way of complex methods like alternative splicing.
An Explanation of RNA Splicing. Gene splicing is a post-transcriptional modification in which a single gene can code for multiple proteins. An animation shows alternate splicing of the SMN2 gene.
It is mostly a cotranscriptional process during which the noncoding introns are excised from pre-mRNA molecules and the flanking exons are spliced together resulting in translation-competent mature mRNA molecules Patel and Steitz 2003. The process is entirely chemical with restriction enzymes used as chemical scissors. A process known as alternative splicing allows for different combinations of exons to be included in the final mature mRNA making different versions of proteins called.
RNA splicing is a process in molecular biology where a newly-made precursor messenger RNA pre-mRNA transcript is transformed into a mature messenger RNA It works by removing all the introns non-coding regions of RNA and splicing back together exons coding regions. RNA processing such as splicing capping and poly-A tail addition. Plasmids are cut with the same restriction enzyme from step 1.
Chopping out of introns or junk sequences and pasting together of the remaining good sequences exons Once its completed these steps the RNA is a mature mRNA. The example of a gene with a single intron and two exons used above is a very simple model of RNA splicing. Messenger RNA mRNA translation and lifetime in the cytosol.
For nuclear-encoded genes splicing occurs in the nucleus either during or immediately after. Gene Splicing Overview Techniques Gene Splicing Introduction. Pre-mRNA splicing is an essential step in gene expression.
In the sections below well discuss some common types of gene regulation that occur after an RNA transcript has been made. 2D Animation of Alternative RNA Splicing. Gene Splicing is done in eukaryotes prior to mRNA translation by the differential inclusion or exclusion of regions of pre-mRNA.
Identifying and isolating a gene that creates a desired protein geneticists place the gene into a vector plasmid and then insert it into a host cell usually bacteria. How does methylating DNA alter chromatin structuregene expression. - Human DNA cut into fragments using a restriction enzyme.
Addition of a 5 cap to the beginning of the RNA. There are a couple ways to. References Gene Splicing.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. The gene is separated by using restriction enzymes to cut the DNA into fragments or polymerase chain reaction PCR to amplify up the gene segment. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
A variety of different recombinant DNA technology is used in modern science including gene splicing electroporation and chemical transformation. Alternative splicing is a process to differentially link exon regions in a single precursor mRNA to produce two or more different mature mRNAs a strategy frequently used by higher eukaryotic cells to increase proteome diversity andor enable additional post-transcriptional control of. Through transformation recombinant plasmids enter bacterial c.
The cell containing the gene is opened and the DNA is purified. View the full answer.

Dna Splicing An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Gene Splicing Mechanism Alternative Splicing Tutorial Splice Variant Detection

No comments for "Describe the 6 Step Process Used in Gene Splicing"
Post a Comment